4 early signs of viral infections
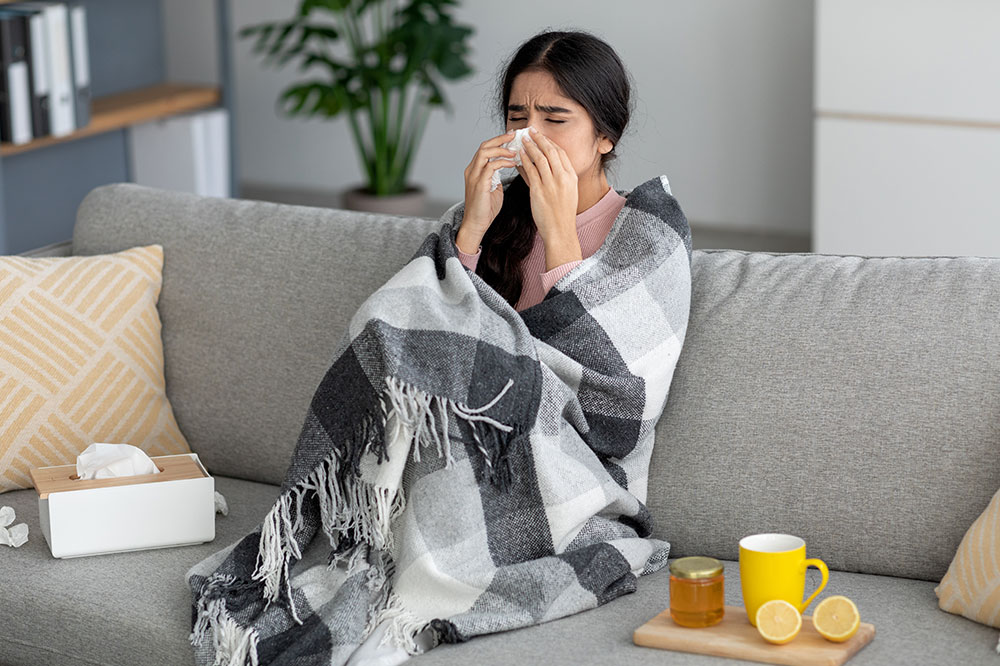

A viral infection can seem similar to a bacterial infection because of an overlap in their symptoms. However, viruses are much tinier than bacteria and need a host to survive, making treatment of viral infections differ from bacterial ones. Viruses can cause many diseases by attacking certain cells like those in the respiratory system, liver, and blood. Here are a few early signs of a viral infection that one can observe:
Flu symptoms
Fever, body aches, headache, and fatigue are some of the telltale signs of a viral infection like influenza. These symptoms can vary from mild to severe and may require immediate treatment. The symptoms here may develop suddenly instead of gradually, so it is important to seek a prompt diagnosis when one observes any of the abovementioned signs. Those with flu symptoms usually recover in less than two weeks, however, some people may experience serious complications like pneumonia.
Upper respiratory symptoms
Another common type of symptom to recognize is respiratory issues, like persistent sore throat, coughing, nasal congestion, and sneezing. Sinus or ear infections are some of the complications that can develop due to a viral infection. In severe cases, the virus can cause extreme inflammation in the respiratory system, which can lead to sepsis—the body’s extreme response to an infection. It is referred to as an emergency situation requiring immediate treatment. Usually, the reaction starts in the lung and moves on to the urinary tract, skin, and gastrointestinal tract. Without immediate intervention, sepsis may lead to tissue damage and organ failure.
Digestive issues
When dealing with a viral infection, one may experience digestive problems like vomiting, nausea, and also diarrhea. Also known as stomach flu, viral gastroenteritis is an infection in the intestines. Having contaminated water or unhygienic food are common risk factors for this disease, so one of the best ways to prevent the onset of this viral infection is to avoid food and drinks that have unknown ingredients and are not prepared in a sanitized setting. One should also wash hands thoroughly before eating anything. Those with good immunity may be able to fight the infection, but those with compromised immunity may need longer to recover. Stomach flu symptoms usually develop 1 to 3 days after the virus has entered the body and can range from mild to severe.
Skin problems
Rashes, sores, warts, and blisters may also be early signs of a viral infection attacking the skin. Sometimes the virus is in the body, and other times it could affect the skin and find other hosts upon contact. A few examples of viral skin infections are measles or German measles; hand, foot, and mouth disease; chickenpox; monkeypox cold sores; herpes.
These viruses can enter the body through the nose, mouth, eyes, anus, genitals, and skin (injured or broken). So, one should be mindful of the surroundings, practice good hygiene, choose safe food and water sources, and wash their hands thoroughly before and after meals. Covering the nose and the mouth with a mask can also help. One should also sanitize and disinfect daily-use surfaces and hands frequently.