Overactive bladder – Foods to avoid

Overactive bladder, also commonly known as OAB, is characterized by the frequent and sudden urge to pass urine, which cannot be controlled. Those with this condition may also experience urgency incontinence or unintentional loss of urine. One’s eating habits can help a great deal in managing an overactive bladder. On that note, here is a list of four foods to avoid or restrict to reduce the symptoms of an overactive bladder.
Foods to avoid
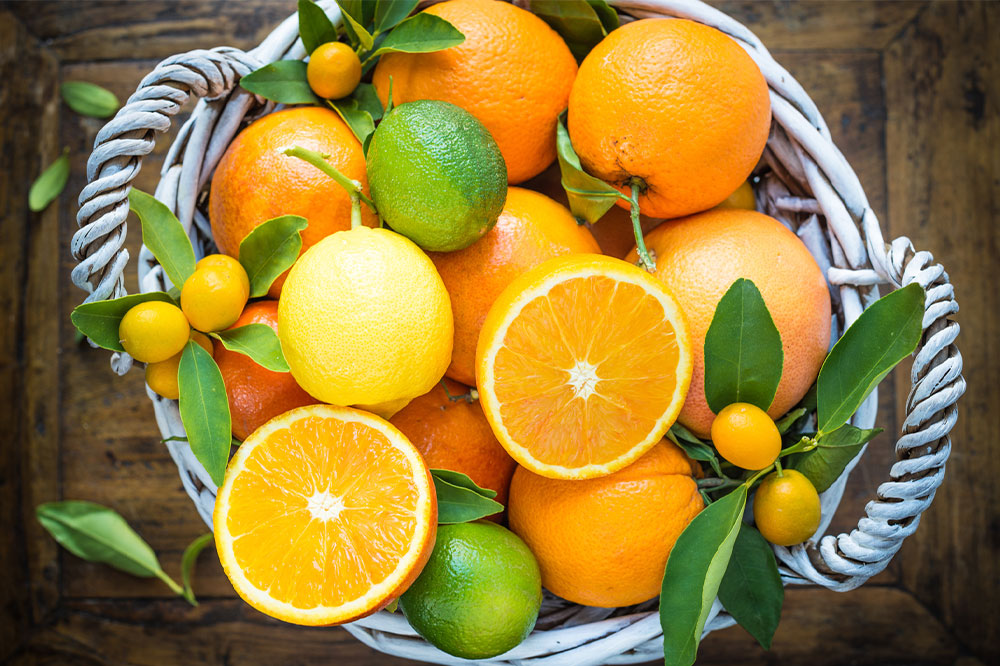
Citrus fruits like oranges
Fruits with high concentrations of acid are considered to be trigger foods for those with an overactive bladder. The acid in oranges, lemons, grapefruits, and limes irritates the inner lining of the bladder. Hence, it is essential to consume them in moderation. The list also covers juices and lemonades.
Caffeine
Caffeinated beverages are among the most common foods that contribute to an overactive bladder. The caffeine in tea and coffee acts as a bladder stimulant and increases the frequency of passing urine. It is advisable to lower the consumption of caffeinated beverages to avoid aggravating the symptoms of bladder incontinence.
Artificial sweeteners
Foods rich in sugar and artificial sweeteners like sodas, pastries, icecreams, and sugar-free desserts should be avoided or limited. Artificial sweeteners like aspartame, sodium saccharin, and acesulfame K, which are usually used in frozen desserts, increase urinary frequency and urgency. They irritate the bladder and aggravate the symptoms of OAB.
Soft drinks
Soft drinks contain caffeine, sweeteners, and carbonation. Besides caffeine and sweeteners, carbonated drinks belong on the list of things that should not be consumed by those with an overactive bladder, as they aggravate the condition.
There are other ways to manage bladder incontinence in addition to foods and fluids that should be restricted from one’s food regime. These include Gemtesa and Myrbetriq, which are prescribed by a doctor to reduce the symptoms of the condition. Some of these treatment methods for an overactive bladder are mentioned below.
Gemtesa®
GEMTESA®, a popular OAB treatment option, has vibegron as its primary component. It is a beta-3 antagonist responsible for decreasing the frequency or preventing bladder contractions. It is taken orally and under the guidance of a licensed medical professional.
Myrbetriq®
This is commonly used to manage the symptoms of an overactive bladder. MYRBETRIQ® is a beta-3 antagonist that helps fight the condition by relaxing the smooth muscles around the bladder and decreasing the number of bathroom trips. MYRBETRIQ is available in the form of granules and pills and is prescribed based on the patient’s condition.